| Citation: | Wang Le Yi, McKelvey George M., Wang Hong. Multi-outcome predictive modelling of anesthesia patients[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2019, 33(6): 430-434. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.33.20180088 |
Anesthesia decisions during surgery involve controlling and maintaining a patient's anesthetic depth, blood pressures and heart rate, among many other conditions. This decision process relies on sound experience of estimating the impact of the drug inputs on the patient outcomes. Accurate estimation of such drug impacts is difficult due to several factors[1–2]: typically, an anesthesia drug can affect multiple outcomes; the same drug can have differing impacts on different patients; the impacts can be altered by surgical types, procedures, stages, and patient conditions; drug-to-drug interactions can influence patient outcomes. For anesthesiologists, management of such parameters on daily basis with accuracy and safety significantly depends on training and experience. Based on our increasing knowledge of drug interactions, it is essential to identify measurable relationships between drug administration and corresponding patient outcomes in a more accurate, objective, and reliable format[3].
Advanced information processing technology can be of great value in this pursuit. For instance, mathematical models can be developed and embedded into anesthesia monitoring systems so that in addition to "monitoring" the current status of a patient, they also can provide a prediction of the patient outcomes in the near-future. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques and machine learning are also highly suitable in this application since they can use real-time observed data to modify models so that the models can become individualized to the specific patient, and the given type and stage of the surgery.
We report here an effort in developing such a new technology. The core of this technology is a data-based mathematics function model that relates multiple drugs and their interactions to several essential predictive outcomes of surgical patients in the near-future. This predictive capability can then be employed to display the patient's current status along with predictive near-future outcome trajectories. When a drug infusion rate is modified, its estimated impact can be immediately displayed. As a result, if a specifically targeted anesthesia depth or blood pressure level is required, this function can be used to display a computer-assisted "trial" on the system to ensure that the targeted factors can be achieved within required timeframes before the actual drug is administered to the patient.
It is noted that the importance of outcome prediction has been recognized in many procedures in anesthesiology and several scoring methods were employed, including Surgical Apgar[4], Risk Stratification Tools for predicting morbidity and mortality[5], and Preoperative Score for predicting postoperative mortality[6]. Computer-assisted outcome prediction and decision assistance are more challenging, and have attracted more attention. Trauma resuscitation errors and their corrections were investigated with AI technology[7]. General discussions on feasibility of AI technology for automated anesthesia drug delivery were reported[8]. These studies have different focuses, use different methods, and report different results in this paper.
The study was approved by the appropriate Institutional Review Board and written informed consents were obtained from all subjects[2]. We selected a patient population between 20 and 70 years of age (n=7), undergoing upper extremity arteria-venous fistula placement or thrombectomy, under intravenous unconscious sedation. Prior to surgery each patient was given 1 mg of Midazolam Ⅳ, taken to the operating room, and equipped with a bispectral (BIS) monitor (Aspect Medical Devices, Inc.), noninvasive blood pressure (BP) cuff, and pulse oximeter. BIS (streamed continuously) and BP (measured every three minutes) data were used in this study. As the interaction between BIS depth and BP are commonly observed patient data in anesthesia administration, we selected these two parameters as a suitable platform to start and to potentially expand to include others such as heart rate, etc. The data from each patient is divided into two time segments with the first time interval a duration of 30%–50% of the entire data collection time. The first segment is used to establish the model, namely determining the model parameters. The second time segment serves as an independent data for validation. The model fitness is evaluated by comparing the data and the model output for the entire time interval.
The patient was given 1 –2 μg/kg of bolus Ⅳ fentanyl at the beginning of the surgery and a 1 μg/kg bolus during the surgery, if required. The patient started on intravenous propofol pump at a rate of 50 μg/(kg·minute) and titrated as required during the surgery. A BIS sensor was placed on the patient's forehead before administering anesthesia to the patient. The sensor is connected to the BIS monitor, which in turn was connected to a computer to allow continuous recording and saving of the BIS values. A baseline BIS value of at least 90 is recorded before the administration of anesthesia. All measured heart rates and blood pressures values were entered and saved manually into the computer every three minutes and following any bolus administration. The propofol rate, any changes made to the propofol rate, and any propofol or fentanyl bolus given are also transmitted to the computer model. Data from seven patients were recorded. The BIS range from 0 (no or minimal brain activity) to 100 (patient fully awake and aware), is set by the device manufacturer. As a data collection system, the internal BP limits in the computer system is set on a wide range so as not to disturb or affect data entry. Data for each patient were reviewed by an experienced anesthesiologist for any possible anomalies or errors.
The core function of this new monitoring technology is framed in establishing reliable embedded computer modelling that can directly correlate the drug or procedure inputs to outcomes in a surgery or procedure. The model structure must be capable of capturing the essential features of a patient's response to the drugs in such a manner that it is able to calculate how the past and current drug infusion rates will result in outcome changes in the immediate future. The model must be tunable to fit specific patient parameters into a varied range of surgical procedures. Here the capability of "AI" is used in the broad sense in which the model parameters are learned from data by certain identification or learning algorithms.
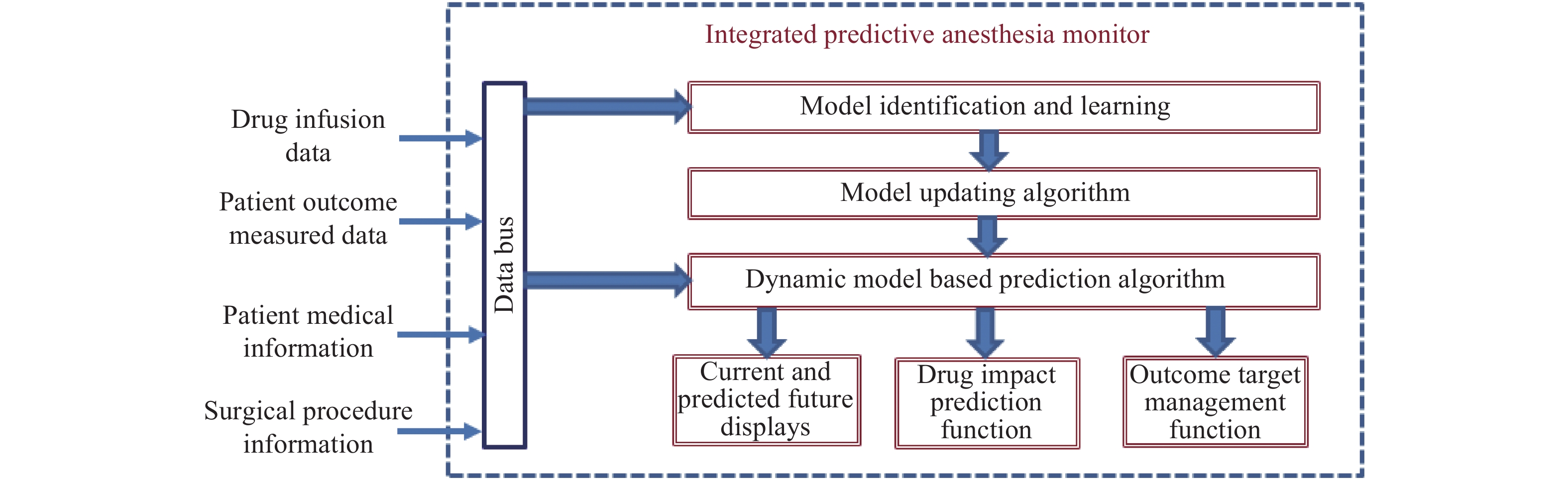
The function modules of this technology are depicted in Fig. 1. The drug infusion data and patient outcomes were measured by the medical devices, and streamed to the computer for processing. The computer model inputs further patient and surgical information to develop short-term predictive outcomes. The display module shows both the current status and predicted outcomes on the screen with both numerical values and graphical trend curves. Fig. 2 is a collaborative display of anesthesia depth (BIS) and blood pressure. The system additionally contains a decision-assistant function module that allows the anesthesiologist to enter planned drug modifications and the system to generate a predicted impact of such changes. Tuning such modifications can allow the anesthesiologist to develop suitable scenarios to have patient outcomes designed to achieve desired target values at specific times.
To make the model account for patient uniqueness, the learning function uses the observed data to tune the model parameters, leading to a data-based learning capability. In our early work[2], a specially designed computer monitoring system was developed to record multi-drug-multiple-outcome data. The data observed a clear correlated outcome response to propofol titration, bolus injection and fentanyl injection: the anesthesia drugs lower the patient BIS values, depress blood pressure, and result in higher heart rate fluctuations.
To capture such dynamic relationships, we are developing an enhanced modelling technique which involves the following function modules: (1) The drug input function module to represent the drug-administering system, injection pathway, and propagation to the blood; (2) The dynamic system module to capture the common feature of initial delay and gradual impact of the drug on outcomes; (3) The multi-output function module to model the impact of the drug on each considered outcome.
The basic model structure is called a "Wiener Model"[3,9], which relates an input to an output and contains three generic blocks: time delay, dynamic delay, and sensitivity function. It can be used for different inputs and outputs such as propofol-to-BIS relationship. For each application, the parameters will be different in different patients, which are estimated by data.
This model structure was further expanded to include multiple inputs and multiple outputs, and called a multi-input-multi-output Hammerstein-Weiner model in engineering. It extends our previous work of using single-input-single-output Wiener models[3,9−10] which do not involve the drug input function, to the multi-drug-multi-outcome framework here. By using the simplified but representative dynamics and functions to represent these relationships, we ensure that the model contains only a relatively small set of parameters that can be updated and learned in real time during a surgery.
Our approach for determining the parameter values is data-based learning and system identification. In our early work[11], we used a special identification algorithm to learn model parameters. In this approach, we first use the patient condition and population-based model as the initial parameter values. After the drug administration is performed, the system starts to receive data on the drug infusion and the patient outcomes, which are used to modify the parameter values. The algorithms used to perform this task are called system identification algorithms.
The distinct advantages and contributions of our approach are in the following aspects: (1) Since simplified dynamic and function models are used, less data is required to update the parameters so that the model can more rapidly capture the salient characteristics of a specific patient, under a specific surgery, at a specific time; (2) By including the drug input functions, our model can capture data from diversified medical devices by multiple manufacturers with multiple differing device features; (3) By including multiple drugs and multiple outcomes in a unified model, we can represent interactions of drugs and their correlated impact on patient outcomes under a unified monitor system.
In our study, we used a simple-structured dynamic model that mainly captured the drug impact in the following aspects: the effects of drug changes on the BIS and BP, the time delay before the initial visible response, and the response speed of the drug effect on the BIS and BP. Mathematically, this can be written as a three-component cascaded system: a time delay of
As shown in Fig. 3, with recorded data and our system's predicted outcome values, BIS values can be affected by many unknown factors, such as surgery stimulation, and body movement, among many others. The system's capability was reflected by its prediction of the main trend of BIS values as responses to drug administration. The curves showed desirable features of the system. The BP data were collected every three minutes. The curves outline that propofol affected the BP, but with slightly less impact than the fentanyl injection.
There have been extensive efforts in studying automated anesthesia administration by using feedback control techniques[12–18]. These population-based models lack the ability of "learning" in real time to generate patient-specific models. The multi-outcome predictive monitoring technique described here is a fundamental improvement on the current anesthesia monitoring technology by providing critical future-impact information, manageable reliability, and useful decision assistance. The main ideas of using mathematics models, signal processing, and individualized management to improve anesthesia care have been used in other related areas of anesthesiology[19–21]. This report highlights a promising approach to addressing several critical requirements for such a new technology: simple and reliable models, data-based and individualized patient outcome monitoring and prediction, and learning capability.
| [1] |
Nakayama M, Ichinose H, Yamamoto S, et al. The effect of fentanyl on hemodynamic and bispectral index changes during anesthesia induction with propofol[J]. J Clin Anesth, 2002, 14(2): 146–149. doi: 10.1016/S0952-8180(01)00375-0
|
| [2] |
Tan ZB, Kaddoum R, Wang LY, et al. Decision-oriented multi-outcome modeling for anesthesia patients[J]. Open Biomed Eng J, 2010, 4: 113–122. doi: 10.2174/1874120701004010113
|
| [3] |
Wang LY, Yin GG, Wang H. Identification of wiener models with anesthesia applications[J]. Int J Pure Appl Math Sci, 2004, 3: 35–61.
|
| [4] |
Cihoric M, Tengberg LT, Bay-Nielsen M, et al. Prediction of outcome after emergency high-risk intra-abdominal surgery using the surgical Apgar score[J]. Anesth Analg, 2016, 123(6): 1516–1521. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001501
|
| [5] |
Moonesinghe SR, Mythen MG, Das P, et al. Risk stratification tools for predicting morbidity and mortality in adult patients undergoing major surgery: qualitative systematic review[J]. Anesthesiology, 2013, 119(4): 959–981. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182a4e94d
|
| [6] |
Le Manach Y, Collins G, Rodseth R, et al. Preoperative score to predict postoperative mortality (POSPOM): derivation and validation[J]. Anesthesiology, 2016, 124(3): 570–579. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000972
|
| [7] |
Fitzgerald M, Cameron P, Mackenzie C, et al. Trauma resuscitation errors and computer-assisted decision support[J]. Arch Surg, 2011, 146(2): 218–225. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2010.333
|
| [8] |
Grassi FR, Rapone B, Catanzaro FS, et al. Effectiveness of computer-assisted anesthetic delivery system (STATM) in dental implant surgery: a prospective study[J]. ORAL Implantol, 2017, 10(4): 381–389. doi: 10.11138/orl/2017.10.4.381
|
| [9] |
Wang LY, Wang H, Yin GG. System for identifying patient response to anesthesia infusion: US, 8998808[P]. 2015-04-01.
|
| [10] |
Wang LY, Wang H, Yin GG. Anesthesia infusion models: knowledge-based real-time identification via stochastic approximation[C]//Proceedings of the 41st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2002.
|
| [11] |
Gentilini A, Rossoni-Gerosa M, Frei CW, et al. Modeling and closed-loop control of hypnosis by means of bispectral index (BIS) with isoflurane[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2001, 48(8): 874–889. doi: 10.1109/10.936364
|
| [12] |
Furutani E, Sawaguchi Y, Shirakami G, et al. A hypnosis control system using a model predictive controller with online identification of individual parameters[C]//Proceedings of 2005 IEEE Conference on Control Applications. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2005.
|
| [13] |
Glen JB, Schwilden H, Stanski DR. Workshop on safe feedback control of anesthetic drug delivery. Schloss Reinhartshausen, Germany. June 29, 1998[J]. Anesthesiology, 1999, 91(2): 600–601. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199908000-00067
|
| [14] |
Nunes CS, Mahfouf M, Linkens DA, et al. Modelling and multivariable control in anaesthesia using neural-fuzzy paradigms: Part I. Classification of depth of anaesthesia and development of a patient model[J]. Artif Intell Med, 2005, 35(3): 195–206. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2004.12.004
|
| [15] |
Lin HH, Beck CL, Bloom MJ. On the use of multivariable piecewise-linear models for predicting human response to anesthesia[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51(11): 1876–1887. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.831541
|
| [16] |
Shieh JS, Abbod MF, Hsu CY, et al. Monitoring and control of anesthesia using multivariable self-organizing fuzzy logic structure[M]//Jin YC, Wang LP. Fuzzy Systems in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 273–295.
|
| [17] |
Sreenivas Y, Lakshminarayanan S, Rangaiah GP. Automatic regulation of anesthesia by simultaneous administration of two anesthetic drugs using model predictive control[M]//Magjarevic R, Nagel JH. World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2006–2007. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 82–86.
|
| [18] |
Magjarevic R, Nagel JH. Evaluation of active contour-based techniques toward bone segmentation from CT images[M]// Kim SI, Suh TS. World congress on medical physics and biomedical engineering 2006. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 3121–3125.
|
| [19] |
Wang H, Wang LY, Zheng H, et al. Lung sound/noiseseparation for anesthesia respiratory monitoring. WSEAS Transacts Syst, 2004, 3(4): 1839–1844.
|
| [20] |
Wang H, Wang LY. Continuous intro-operative respiratory auscultation in anesthesia[C]//SENSORS, 2003 IEEE. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2003, 2: 1002–1005.
|
| [21] |
Wang LY, Yin G, Wang H. Wang H. Reliable nonlinear system identification in medical applications[J]. IFAC Proceed Vol, 2003, 36(16): 133–138. doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)34751-1
|
| [1] | Qingqing Li, Chaoqin Wu, Zhenfei Huang, Jiang Cao, Jie Chang, Guoyong Yin, Lipeng Yu, Xiaojian Cao, Tao Sui. A comparison of robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-assisted kyphoplasty in the treatment of multi-segmental osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2022, 36(3): 208-214. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.36.20220023 |
| [2] | Jiao Chen, Can Zhao, Yingzi Huang, Hao Wang, Xiang Lu, Wei Zhao, Wei Gao. Malnutrition predicts poor outcomes in diabetic COVID-19 patients in Huangshi, Hubei[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2022, 36(1): 32-38. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.35.20210083 |
| [3] | Li Chaoyun, Meng Ping, Zhang Benzheng, Kang Hong, Wen Hanli, Schluesener Hermann, Cao Zhiwei, Zhang Zhiyuan. Computer-aided identification of protein targets of four polyphenols in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and validation in a mouse AD model[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2019, 33(2): 101-112. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.32.20180021 |
| [4] | Huan Liu, Shijiang Zhang, Yongfeng Shao, Xiaohu Lu, Weidong Gu, Buqing Ni, Qun Gu, Junjie Du. Biomechanical characterization of a novel ring connector for sutureless aortic anastomosis[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2018, 32(6): 454-460. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.31.20170011 |
| [5] | Dominik Choromanski, Joel Frederick, George Michael Mckelvey, Hong Wang. Intraoperative patient information handover between anesthesia providers[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2014, 28(5): 383-387. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.28.20140001 |
| [6] | Rajiv Shrestha, Jing Xu, Dujiang Xie, Zhizhong Liu, Tian Xu, Fei Ye, Shiqing Din, Xuesong Qian, Song Yang, Yueqiang Liu, Feng Li, Aiping Zhang, Shaoliang Chen. Comparison of clinical outcomes of Chinese men and women after coronary stenting for coronary artery disease: a multi-center retrospective analysis of 4,334 patients[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2014, 28(5): 368-375. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.28.20120127 |
| [7] | Weihua Zhou, Ji Chen. I -123 metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging for predicting ventricular arrhythmia in heart failure patients[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2013, 27(6): 460-466. DOI: 10.7555/JBR.27.20130137 |
| [8] | Tongfu Yu, Mei Yuan, Qingbo Zhang, Haibing Shi, Dehang Wang. Evaluation of computed tomography obstruction index in guiding therapeutic decisions and monitoring percutanous catheter fragmentation in massive pulmonary embolism[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2011, 25(6): 431-437. DOI: 10.1016/S1674-8301(11)60057-2 |
| [9] | Keh-Dong Shiang, Fouad Kandeel. A computational model of the human glucose-insulin regulatory system[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2010, 24(5): 347-364. DOI: 10.1016/S1674-8301(10)60048-6 |
| [10] | Tingting Zhao, Ren Zhang, Mingbo Wang. Prediction of candidate small non-coding RNAs in Agrobacterium by computational analysis[J]. Journal of Biomedical Research, 2010, 24(1): 33-42. |